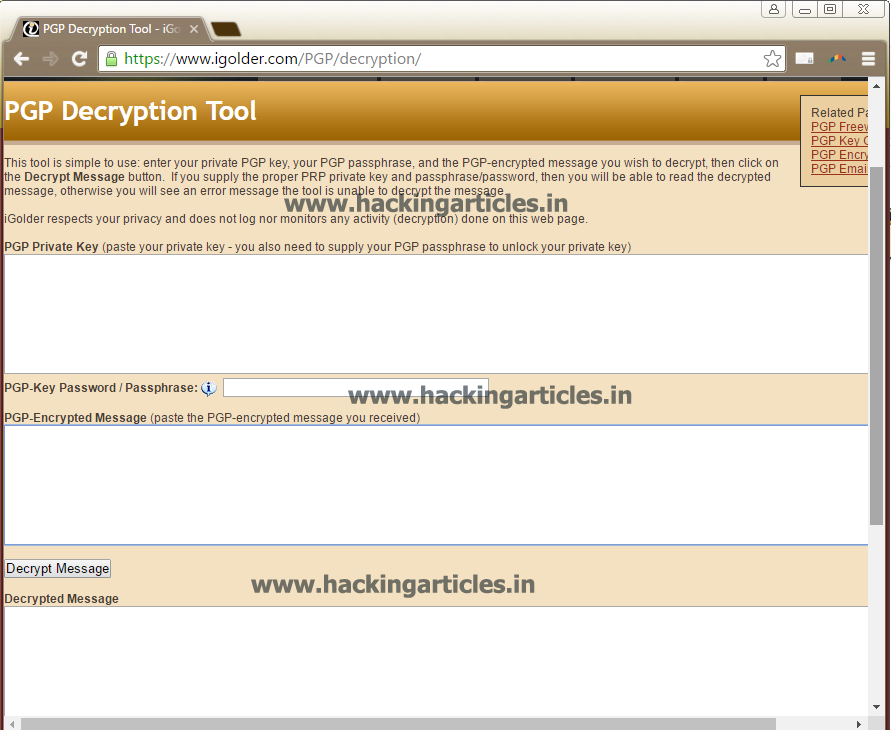
Pgp Decryption Tool
Those of you who nominated VeraCrypt praised it for being an on-the-fly encryption tool, as in your files are only decrypted when they're needed and they're encrypted at rest at all other times, and most. GNU Privacy Guard (GnuPG) is actually an open-source implementation of Pretty Good Privacy (PGP). OpenPGP is the most widely used email encryption standard. It is defined by the OpenPGP Working Group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as a Proposed Standard in RFC 4880.OpenPGP was originally derived from the PGP software, created by Phil Zimmermann.
Concerning the PGP Key Generator, we DO NOT record any data: no e-mail address, no password and no messages. If you wish to place an order, your details will be requested. Some services require the use of cookies to work, and these cookies can not be disabled: - The very site of wp2pgpmail, if you identify yourself by logging into your account.
How PGP encryption works PGP encryption uses a serial combination of, and finally; each step uses one of several supported. Each public key is bound to a user name or an address. The first version of this system was generally known as a to contrast with the system, which uses a hierarchical approach based on and which was added to PGP implementations later.
Current versions of PGP encryption include both options through an automated key management server. Compatibility As PGP evolves, versions that support newer features and algorithms are able to create encrypted messages that older PGP systems cannot decrypt, even with a valid private key. Therefore, it is essential that partners in PGP communication understand each other's capabilities or at least agree on PGP settings. Confidentiality PGP can be used to send messages confidentially. For this, PGP combines symmetric-key encryption and public-key encryption. The message is encrypted using a symmetric encryption algorithm, which requires a symmetric key. Each symmetric key is used only once and is also called a session key.
The message and its session key are sent to the receiver. The session key must be sent to the receiver so they know how to decrypt the message, but to protect it during transmission it is encrypted with the receiver's public key. Only the private key belonging to the receiver can decrypt the session key. Digital signatures PGP supports message authentication and integrity checking.
The latter is used to detect whether a message has been altered since it was completed (the message integrity property) and the former to determine whether it was actually sent by the person or entity claimed to be the sender (a ). Because the content is encrypted, any changes in the message will result in failure of the decryption with the appropriate key. The sender uses PGP to create a digital signature for the message with either the or algorithms. To do so, PGP computes a hash (also called a ) from the plaintext and then creates the from that hash using the sender's private key. Web of trust.
This section contains content that is written like. Please help by removing and inappropriate, and by adding encyclopedic content written from a. (November 2017) For the enterprise, currently offers the only commercial versions of PGP for the and mainframe platforms.
Townsend Security became involved with PGP encryption in 2000 when the company partnered with Network Associates and ported PGP encryption to the IBM i platform. Later in 2008 Townsend Security ported PGP to the IBM z mainframe. IBM z supports PGP with z/OS encryption facility, which is available for free and uses hardware acceleration.
PGP Corporation encryption applications This section describes commercial programs available from. For information on other programs compatible with the specification, see below. While originally used primarily for encrypting the contents of e-mail messages and attachments from a desktop client, PGP products have been diversified since 2002 into a set of encryption applications which can be managed by an optional central policy server. PGP encryption applications include e-mail and attachments, digital signatures, laptop full disk encryption, file and folder security, protection for IM sessions, batch file transfer encryption, and protection for files and folders stored on network servers and, more recently, encrypted or signed HTTP request/responses by means of a client-side and a server-side module. There is also a Wordpress plugin available, called wp-enigform-authentication, that takes advantage of the session management features of Enigform with modopenpgp.
The PGP Desktop 9.x family includes PGP Desktop Email, PGP Whole Disk Encryption, and PGP NetShare. Additionally, a number of Desktop bundles are also available. Depending on application, the products feature desktop e-mail, digital signatures, IM security, whole disk encryption, file and folder security, encrypted, and of deleted files. Capabilities are licensed in different ways depending on features required.
The PGP Universal Server 2.x management console handles centralized deployment, security policy, policy enforcement, key management, and reporting. It is used for automated e-mail encryption in the gateway and manages PGP Desktop 9.x clients. In addition to its local keyserver, PGP Universal Server works with the PGP public keyserver—called the PGP Global Directory—to find recipient keys. It has the capability of delivering e-mail securely when no recipient key is found via a secure HTTPS browser session. With PGP Desktop 9.x managed by PGP Universal Server 2.x, first released in 2005, all PGP encryption applications are based on a new proxy-based architecture. These newer versions of PGP software eliminate the use of e-mail plug-ins and insulate the user from changes to other desktop applications. All desktop and server operations are now based on security policies and operate in an automated fashion.
The PGP Universal server automates the creation, management, and expiration of keys, sharing these keys among all PGP encryption applications. The Symantec PGP platform has now undergone a rename. PGP Desktop is now known as Symantec Encryption Desktop, and the PGP Universal Server is now known as Symantec Encryption Management Server. The current shipping versions are Symantec Encryption Desktop 10.3.0 (Windows and Mac OS platforms) and Symantec Encryption Server 3.3.2. Also available are PGP Command Line, which enables command line-based encryption and signing of information for storage, transfer, and backup, as well as the PGP Support Package for BlackBerry which enables RIM BlackBerry devices to enjoy sender-to-recipient messaging encryption.
New versions of PGP applications use both OpenPGP and the, allowing communications with any user of a specified standard. OpenPGP Inside PGP Inc., there was still concern about patent issues. RSADSI was challenging the continuation of the Viacrypt RSA license to the newly merged firm. The company adopted an informal internal standard they called 'Unencumbered PGP' which would 'use no algorithm with licensing difficulties'. Because of PGP encryption's importance worldwide, many wanted to write their own software that would interoperate with PGP 5. Zimmermann became convinced that an open standard for PGP encryption was critical for them and for the cryptographic community as a whole.
In July 1997, PGP Inc. Proposed to the that there be a standard called OpenPGP. They gave the IETF permission to use the name OpenPGP to describe this new standard as well as any program that supported the standard. The IETF accepted the proposal and started the OpenPGP. OpenPGP is on the and is under active development.
Many e-mail clients provide OpenPGP-compliant email security as described in. The current specification is (November 2007), the successor to. Specifies a suite of required algorithms consisting of, and. In addition to these algorithms, the standard recommends as described in v1.5 for encryption and signing, as well as, and.
Beyond these, many other algorithms are supported. The standard was extended to support cipher by in 2009, and signing and key exchange based on (i.e. And ) by in 2012. Support for encryption was added by the proposed in 2014. The has developed its own OpenPGP-compliant program called (abbreviated GnuPG or GPG). GnuPG is freely available together with all source code under the (GPL) and is maintained separately from several Graphical User Interfaces that interact with the GnuPG library for encryption, decryption and signing functions (see, ).
Several other vendors have also developed OpenPGP-compliant software. The development of an opensource OpenPGP-compliant library, OpenPGPjs, written in has allowed web based applications to use PGP encryption in the web browser. There are several iOS and Android OpenPGP-compliant applications such as iPGMail for iOS and OpenKeychain for Android, which enable key generation and encryption/decryption of email and files on Apple's iOS and Google's Android. PGP.
PGP Message Exchange Formats (obsolete). OpenPGP. OpenPGP Message Format (obsolete).
OpenPGP Message Format. The Camellia Cipher in OpenPGP.
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) in OpenPGP. OpenPGP Message Format. PGP/MIME. MIME Security with Pretty Good Privacy (PGP). MIME Security with OpenPGP OpenPGP's encryption can ensure secure delivery of files and messages, as well as provide verification of who created or sent the message using a process called digital signing. The open source office suite implemented document signing with OpenPGP as of version 5.4.0 on Linux.
Using OpenPGP for communication requires participation by both the sender and recipient. OpenPGP can also be used to secure sensitive files when they're stored in vulnerable places like mobile devices or in the cloud. Limitations With the advancement of cryptography, parts of PGP have been criticized for being dated:. The long length of PGP public keys.
Difficulty for the users to comprehend and poor usability. Lack of ubiquity In October 2017, the was announced that affects RSA keys generated on the 4 tokens, often used with PGP. Many published PGP keys were found to be susceptible. See also. Essays on PGP. Philip Zimmermann. (October 9, 1995).

Applied Cryptography.:. Messmer, Ellen (August 28, 2000). Retrieved May 2, 2017 – via Google Books.
Nichols, Randall (1999). ICSA Guide to Cryptography. Retrieved 2010-02-08. McCullagh, Declan (July 10, 2007). Retrieved 2010-02-08. May 26, 2003.
Retrieved 2010-02-08. McCullagh, Declan (December 14, 2007). Retrieved 2010-02-08. McCullagh, Declan (January 18, 2008). Retrieved 2010-02-08.
McCullagh, Declan (February 26, 2009). Retrieved 2009-04-22. John Leyden (November 14, 2007). The Register. Chris Williams (November 24, 2009). The Register.
Holtsnider, Bill; Jaffe, Brian D. Phil Zimmermann. Retrieved 2010-08-23. PGP Source Code and Internals. US Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security.
Retrieved December 4, 2011. Retrieved 2015-03-24. ^ 'McAfee partners with Software Diversified Services to deliver E-Business Server sales and support.' Retrieved 2015-06-30.
^ 'Long Live E-Business Server for Enterprise-Scale Encryption.' Software Diversified Services. Retrieved 2015-06-30.
Retrieved 2013-08-06. Retrieved 2013-08-06. January 26, 2010. Retrieved 2013-08-06. Retrieved 2012-03-23. April 29, 2010. Retrieved 2010-04-29.
Pgp Decryption Tool Mac
September 23, 2012. Retrieved 2013-08-06. OpenPGPjs-Team. OpenKeychain-Team. Thorsten's Weblog.
28 July 2017. Retrieved 10 December 2017.
By Eric Geier, PCWorld. “.” August 22, 2014. September 3, 2014. Green, Matthew (August 13, 2014). A Few Thoughts on Cryptographic Engineering. Retrieved December 19, 2016.
^ Marlinspike, Moxie (February 24, 2015). Retrieved December 19, 2016., Matus Nemec, Marek Sys, Petr Svenda, Dusan Klinec,Vashek Matyas, November 2017 Further reading. (December 1, 1991). PGP: Pretty Good Privacy. (January 8, 2001). Lucas, Michael W. (April 1, 2006).
PGP & GPG Email for the Practical Paranoid. (June 1991). Retrieved 2008-03-03. External links.
Online PGP Encryption.
Updated: May 13, 2016 Applies To: System Center 2012 SP1 - Orchestrator, System Center 2012 - Orchestrator, System Center 2012 R2 Orchestrator The PGP Decrypt File activity decrypts a file or entire folder tree using a PGP key file and passphrase that you have created. When decrypting an entire folder, the folder tree is preserved from the root folder down.
For example, if you decrypt C: Documents and Settings Administrator My Documents. and all subfolders, all files in My Documents are decrypted as well as all the files in the folders under My Documents. All files in subfolders will be in the same subfolder in the Output folder. You can use the PGP Decrypt File activity to decrypt files that were encrypted as part of a backup operation. To use this activity you must install the Gpg executable. To install the Gpg executable, see (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=219849). Use the following information to configure the PGP Decrypt File activity.
Details Tab Settings Configuration Instructions Path Type the path of the files that you want to decrypt. You can use wildcards? And.
The Akeytsu 3D animation toolset is designed for both the aspiring artist and the professional animator to produce large volumes of high quality animation quickly and easily. Dedicated solely to rigging and animation, Akeytsu has one of the fastest learning curves of any software in the 3D industry. It provides flexible and. Aug 28, 2014. Let us know and we'll get it added to the list. Morpheme with Euphoria. Company: NaturalMotion. Company: Autodesk. Havok Animation Studio. Company: Havok. Ikinema RunTime. Company: Ikinema. Emotion FX 4. Company: Mystic Game Development. Company: Esoteric Software. Company: Autodesk. The only apps that do make it easy and intuitive are sculpting apps like 3D Coat, or Sculptris, and you can't really use them directly for your game models as they'll produce far too many polygons and will no deform well with animation. So pick a software, and learn it. Seems most people recommend.
to specify the files that you are decrypting. This field will only accept characters from the current system locale. If you use other characters, the activity will fail. Include sub-directories Select this option to find all files that match the file name that you specified in all sub-directories under the folder that you specified in the path. Output folder Type the path of the folder where you want the decrypted files to be stored.
Skip Select this option to skip decrypting a file when a file with the same name is found in the Output folder. Overwrite Select this option to overwrite any files with the same name as a resulting decrypted file.
Pgp Decryption Tool Linux
Create unique name Select this option to give the decrypted file a unique name if a file with the same name already exists. Advanced Tab Settings Configuration Instructions Keyring folder Type the location of the keyring folder that contains the secret keyring file that you will use to decrypt the files. The secret keyring file (.skr) may be renamed with a.gpg extension. Passphrase Type the passphrase that is associated with the keyring file. Published Data The following table lists the published data items. Item Description Keyring folder The path of Keyring folder that contains the key used to decrypt the files. Output folder The path of the folder where the decrypted files were saved.
Pgp File Decryption Tool
Files to decrypt The number of files that Orchestrator attempted to decrypt. Files decrypted The number of files that were successfully decrypted. Decrypted filename The path and filename of the resulting decrypted file.
Latest Pages
- Me And My Broken Heart Download Free
- Download Free Piano Lessons Pdf
- Free Download Sample Swf File
- Street Fighter 2 Rainbow Download
- Cool Edit Pro Portable Windows 7
- Download Reaper Daw Free
- Printshop Mail Crack Download
- Download Process Control At Polaroid Pdf 825
- Harga Toyota Altis 2002 Manual
- Employee Counseling Forms Free Download
- Free Download Software Hacker Facebook Terbaru Edisi
- Ggsemc Drivers Zip
- Iss Darde Dil Ki Sifarish Female Version Ringtone Free Download
- Flactunes Download Chrome
- How To Install K7 Antivirus In Laptop Without Cd Drive
- So Sophisticated Download Rick Ross
- Powtoon Free Download Crack
- Pastel Partner 2005 Download
- I386 Xp Install
- Brahmand Nayak Serial
- Drivers Ed Book Caroline B Cooney Summary
- Geomorphology A Canadian Perspective 5th Edition Pdf
- Wallap Software Cracker
- Download Game Counter Strike Terbaru Full Version